Description
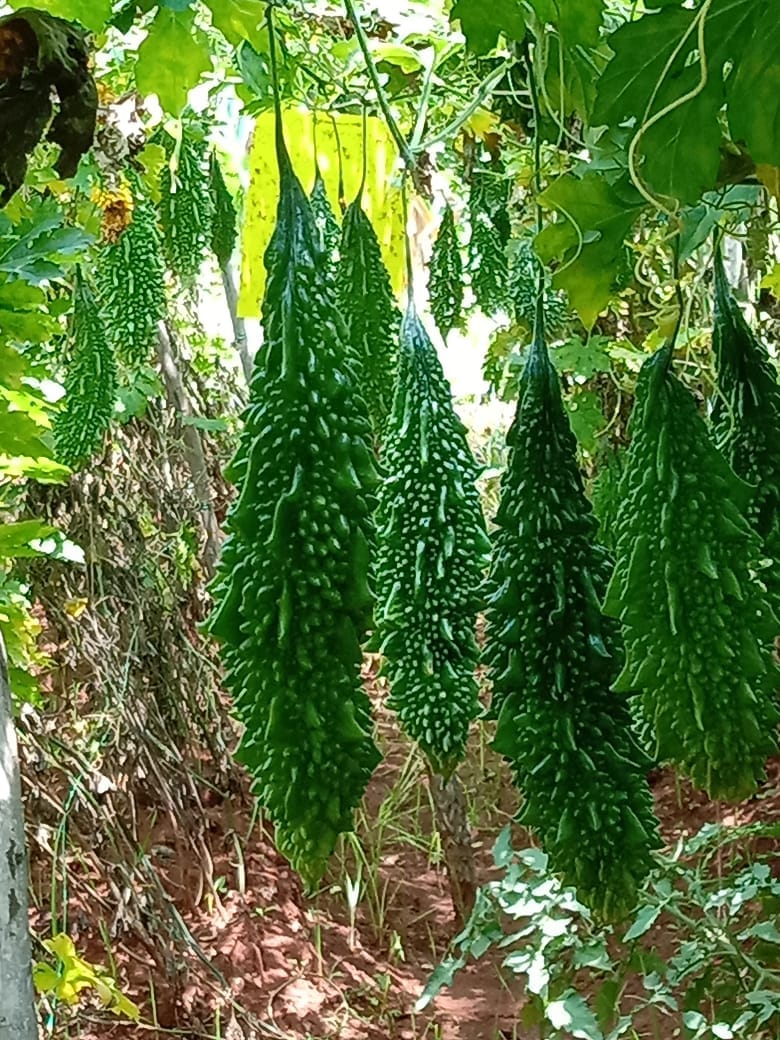
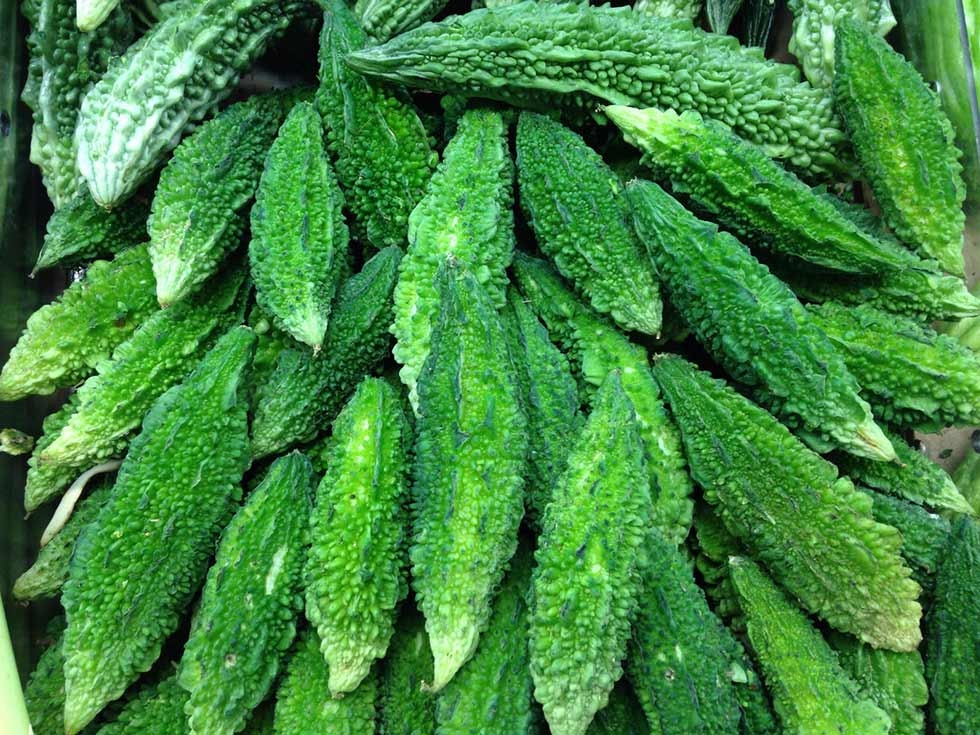
Bitter Gourd (करेला)
Bitter Gourd, also known as bitter melon or करेला in Hindi, is a unique vegetable prized for its distinct bitter taste and extensive health benefits. Despite its bitter flavor, bitter gourd is widely used in culinary traditions across Asia, particularly in Indian, Chinese, and Southeast Asian cuisines.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Rich in Nutrients: Bitter gourd is low in calories but rich in essential nutrients such as vitamins C, A, and K, as well as minerals like iron, magnesium, and potassium.
- Antioxidant Properties: It contains powerful antioxidants like vitamin C and flavonoids, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Bitter gourd is renowned for its potential to lower blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
- Digestive Health: The fiber in bitter gourd supports digestive function and helps promote regular bowel movements.
Health Benefits:
- Diabetes Management: Bitter gourd contains compounds that mimic insulin, helping to regulate blood sugar levels. It also improves glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity.
- Heart Health: The antioxidants and fiber in bitter gourd contribute to heart health by reducing cholesterol levels and promoting a healthy cardiovascular system.
- Immune Support: Vitamin C in bitter gourd supports immune function, helping the body defend against infections and illnesses.
- Liver Health: Bitter gourd is believed to support liver health by aiding in detoxification processes and promoting liver function.
Culinary Uses:
- Cooking Methods: Bitter gourd is often sliced, salted, and left to reduce bitterness before cooking. It can be stir-fried, sautéed, stuffed, or added to soups and curries.
- Regional Dishes: In Indian cuisine, bitter gourd is used in dishes like Karela Sabzi, stuffed bitter gourd (Bharwan Karela), and bitter gourd chips (Karela Chips).
- Medicinal Uses: Bitter gourd is also used in traditional medicine practices for its therapeutic properties, including its role in managing diabetes and improving digestion.
Selection and Storage:
- Choosing Bitter Gourd: Select firm, unblemished bitter gourds that are dark green in color. Smaller gourds tend to be less bitter.
- Storage: Store bitter gourd in a cool, dry place or in the refrigerator wrapped in a paper towel or plastic bag to maintain freshness. Use within a few days for best flavor and texture.
Bitter gourd (करेला) offers a unique flavor profile and a plethora of health benefits, making it a valuable addition to any diet focused on wellness and nutrition.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.